Upload onto CIRM-01: Difference between revisions
From genomewiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
** the "sftp" command is good for basic sftp transfer program of a few files and is installed on most servers and all Mac computers. lftp is using concurrent connections and can be up to 10-20x faster. Lftp is also better in restarting or updating old uploads. | ** the "sftp" command is good for basic sftp transfer program of a few files and is installed on most servers and all Mac computers. lftp is using concurrent connections and can be up to 10-20x faster. Lftp is also better in restarting or updating old uploads. | ||
** see below for examples | ** see below for examples | ||
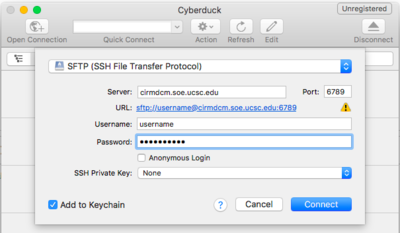
* If you're unsure which program to use, a good choice is CyberDuck on MacOS, see image below on how to connect using CyberDuck | * If you're unsure which program to use and you want a graphical user interface, not a command line program, a good choice is CyberDuck on MacOS, see image below on how to connect using CyberDuck | ||
* Once you're done with the upload, let your wrangler know | * Once you're done with the upload, let your wrangler know | ||
Revision as of 20:02, 6 April 2018
For CIRM groups
- Ask your UCSC wrangler contact person to set you up with a username and password for the cirmdcm.soe.ucsc.edu sftp upload
- Use an sftp command line client like lftp or simply sftp and connect to sftp://cirmdcm.soe.ucsc.edu, port 6789, using this username
- the "sftp" command is good for basic sftp transfer program of a few files and is installed on most servers and all Mac computers. lftp is using concurrent connections and can be up to 10-20x faster. Lftp is also better in restarting or updating old uploads.
- see below for examples
- If you're unsure which program to use and you want a graphical user interface, not a command line program, a good choice is CyberDuck on MacOS, see image below on how to connect using CyberDuck
- Once you're done with the upload, let your wrangler know
Example command line tool "sftp", usually installed on most linuxes and osx, to upload the current directory and all subdirectories:
$ sftp -P 6789 maxSftp@cirmdcm.soe.ucsc.edu sftp> put -r *
Example command line tool "lftp", upload current directory and all subdirectories with 10 concurrent connections ("threads"):
$ lftp sftp://myUsername@cirmdcm.soe.ucsc.edu:6789 > mirror -R --parallel=10
-R stands for "reverse", a reverse mirror is lftp-speak for "upload".
Example graphical user interface, Cyberduck on Mac OSX:
For UCSC Wranglers
On cirm01, create the user:
sudo /data/create-user username
To change password of user:
sudo /data/change-password username
The new user is created with their homedir as:
/data/sftp/user/incoming
You have read access to those directories.